D&C
Your healthcare provider has recommended you have a D&C (dilation and curettage). This common procedure helps your healthcare provider learn more about problems inside your uterus. Or it may be done to treat a miscarriage. During a D&C, the cervix (opening of the uterus) is widened (dilated). Tissue samples are then removed from the endometrium (lining of the uterus) with an instrument called a curette, or with suction. In many cases, D&C is done to find the cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding. Or you may need a D&C as a form of treatment.
A hysteroscopy is usually done along with the D&C for a gynecological problem. A hysteroscopy uses a small instrument to see the inside of the uterus. Hysteroscopy and D&C can be done in the operating room or in the healthcare provider's office, depending on the healthcare provider who does it.
During your D&C
Just before your D&C, you may get medicine to prevent pain. This may be given through an IV. You may be awake but relaxed during the procedure. Or you may be completely asleep. The type of anesthesia used is different depending on where the procedure takes place. The procedure will not start until the pain medicine has taken effect. During your D&C:
-
Instruments are used to hold the vagina open and to steady the uterus. The cervical canal is widened using tapered instruments called dilators.
-
Usually a thin, rigid, or flexible telescope (hysteroscope) is inserted into the vagina to take images of the inside of the uterus. This allows your healthcare provider to see into the uterus.
-
The curette or suction is inserted into the uterus. Tissue samples are taken from several areas. These samples are sent to a lab to be studied.
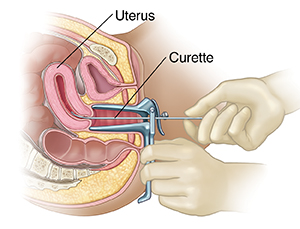 |
| After the cervical canal is dilated, a curette is inserted into the uterus to take tissue samples. |
After your D&C
-
You will rest for a while in a recovery area.
-
You can expect some cramping for a few hours after the D&C. This can be controlled with an over-the-counter pain reliever.
-
You may have some light bleeding for a few weeks. Use pads instead of tampons.
-
Take showers instead of baths for about a week. Ask your healthcare provider if you should stay away from exercising or having sex for a period of time.
Risks and possible complications
D&C rarely causes complications. But as with any procedure, D&C has some risks. Before your D&C, your healthcare provider will discuss these with you. You will be asked to sign a consent form. Risks may include:
-
Infection
-
Heavy bleeding
-
Perforation of the uterine wall or damage to nearby organs
-
Scar tissue may form causing the lining of the uterus to adhere to itself. This can cause problems with menstrual flow or difficulty getting pregnant in the future. This is called Asherman syndrome.
-
The need for additional tests or procedures
-
Risks associated with anesthesia (the medicine that makes you sleep during surgery)
When to call your healthcare provider
Contact your healthcare provider if you have:
-
Heavy bleeding (more than 1 pad an hour)
-
A fever of 100.4°F ( 38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Increasing belly pain, tenderness, or cramping
-
Foul-smelling discharge
Online Medical Reviewer:
Donna Freeborn PhD CNM FNP
Online Medical Reviewer:
Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer:
Irina Burd MD PhD
Date Last Reviewed:
3/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.