Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST)
What is cerebral venous sinus thrombosis?
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) occurs when a blood clot forms in the brain’s venous sinuses. The clot keeps blood from draining out of the brain. As a result, pressure builds up in the blood vessels. This can lead to swelling and bleeding (hemorrhage) in the brain.
This chain of events is part of a stroke that can occur in adults and children. It can occur even in newborns and babies in the womb. A stroke can damage the brain and central nervous system. A stroke is serious and needs medical attention right away.
This condition may also be called cerebral sinovenous thrombosis.
What causes cerebral venous sinus thrombosis?
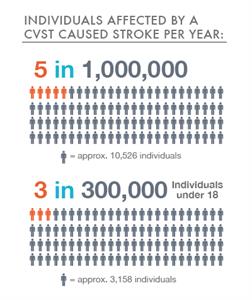
CVST is a rare form of stroke. It affects about 5 people in 1 million each year. The risk for this kind of stroke in newborns is greatest during the first month. Overall, about 3 out of 300,000 children and teens up to age 18 will have a stroke.
Who is at risk for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis?
Children and adults have different risk factors for CVST.
Risk factors for children and infants include:
-
Problems with the way their blood forms clots
-
Sickle cell anemia
-
Chronic hemolytic anemia
-
Beta-thalassemia major
-
Heart disease, which can be congenital (you're born with it) or acquired (you develop it)
-
Iron deficiency
-
Certain infections
-
Dehydration
-
Head injury
-
For newborns, a mother who had certain infections or a history of infertility
Risk factors for adults include:
-
Pregnancy and the first few weeks after delivery
-
Problems with blood clotting such as antiphospholipid syndrome, protein C and S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies, or factor V Leiden mutation
-
Cancer
-
Collagen vascular diseases such as lupus, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and Behcet syndrome
-
Obesity
-
Low blood pressure in the brain (intracranial hypotension)
-
Inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
What are the symptoms of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis?
Symptoms of CVST may vary, depending on where the blood clot is. Responding quickly to these symptoms makes it more possible to recover.
These are the physical symptoms that may occur:
How is cerebral venous sinus thrombosis diagnosed?
People who have had any type of stroke recover best if they get treatment right away. If you suspect a stroke based on the symptoms, have someone take you to the emergency room right away, or call 911 to get help.
Healthcare providers will ask about your health history and do a physical exam. Family and friends can describe the symptoms they saw, especially if the person who had the stroke is unconscious. But the final diagnosis is often made based on how the blood is flowing in the brain. Imaging tests show areas of blood flow. These tests may be used to diagnose CVST:
-
MRI scan
-
CT scan
-
Venography
-
Angiography
-
Ultrasound
-
Blood tests
How is cerebral venous sinus thrombosis treated?
Treatment should begin right away. It must be done in a hospital. A treatment plan could include:
-
Fluids
-
Antibiotics, if you have an infection
-
Medicine to control seizures if they have occurred
-
Monitoring and controlling the pressure inside the head
-
Medicine to stop the blood from clotting (anticoagulants)
-
Surgery
-
Continued monitoring of brain activity
-
Measuring your eyesight and monitoring change
-
Rehab (rehabilitation)
What are possible complications of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis?
Complications of CVST include:
Can cerebral venous sinus thrombosis be prevented?
You can do a lot to prevent stroke by leading a heart-healthy lifestyle:
-
Eat a low-fat diet, including lots of fruits and vegetables.
-
Get daily exercise.
-
Stay away from cigarette smoke.
-
Control chronic health conditions such as diabetes.
Living with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
What you need to do to recover and then stay healthy after CVST will depend on how the stroke affected your brain. Everyone can benefit from a healthy diet and exercise.
You may also need to take part in a special rehab program or physical therapy if you have lost some movement or speech.
Other possible effects of the stroke, such as headaches or changes in vision, can be treated by specialists.
If you have had this type of stroke, you may not be able to take certain types of medicines, such as birth control pills (oral contraceptives). These can increase your risk for blood clots.
Key points about cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
-
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) occurs when a blood clot forms in the brain’s venous sinuses.
-
If you have CVST, respond quickly to symptoms like headaches, blurry vision, fainting, losing control of a part of your body, and seizures.
-
If you have the above symptoms, have someone take you immediately to the emergency room or call 911 for help.
-
Take your medicines as prescribed and check with your healthcare provider to make sure that none of your medicines increase your risk of having CVST.
-
Teach your loved ones about the symptoms of CVST so they can be ready in an emergency.
-
Follow a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a low-fat diet.
-
Exercise every day and don't smoke.
-
Manage other chronic health issues such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
-
Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
-
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
-
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your healthcare provider tells you.
-
At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your healthcare provider gives you.
-
Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are.
-
Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
-
Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
-
Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
-
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
-
Know how you can contact your healthcare provider if you have questions.